Classically, brain monitoring after SAH can be divided into the time spent on the ICU, with the patient supported by ventilation, and afterwards. Brain monitoring in the ICU does not differ generally from monitoring after TBI. After the ICU period, monitoring is mainly focused on the detection of vasospasm and dysutoregulation of blood flow, mainly using transcranial Doppler ultrasongraphy (TCD) or near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS).
ICM+ monitoring in poor grade SAH resembles general multimodal brain monitoring following TBI:
ICP, CPP, PbtO2, and cerebral microdialysis probes are used. ICM+ is used to integrate separate monitors and to calculate secondary indices.
From non-invasive modalities, TCD and NIRS are often used both inside and outside of the NCCU, where daily assessments of autoregulation and spasm are necessary.

Example of continuous monitoring of ICP, CPP, and PbtO2 (from the point of ‘targeted monitoring’, an additional probe was used on the spastic side (dark blue)) . ‘Optimal CPP’ was evaluated during the initial, spasm, and HHH periods with a gradually increasing value of CPPopt. PbtO2 ipsilateral to the spasm improved after introduction of HHH therapy. View image

Primary and secondary indices may be compared with cerebral microdialysis. The LPR ratio ipsilateral to the spastic side (blue) and contralateral side (black) reacting to temporary decrease in ABP
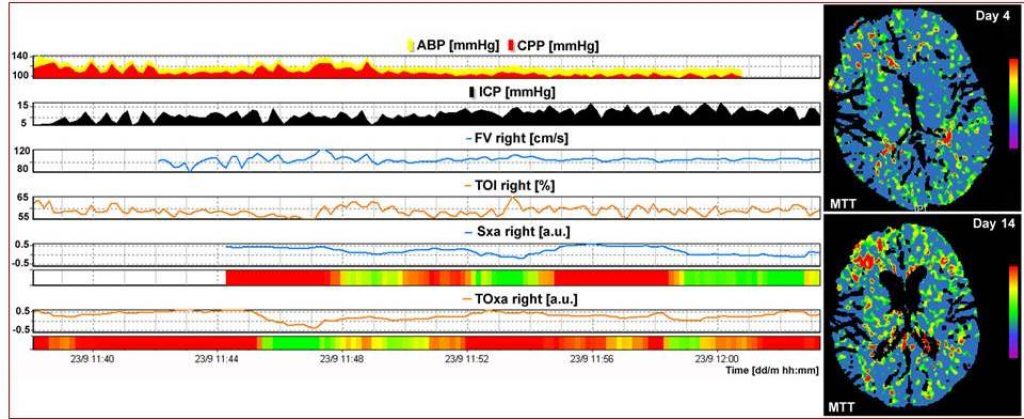
Autoregulation indices calculated intermittently with TCD and NIRS can be easily compared with perfusion CT data (right MCA territory spasm).
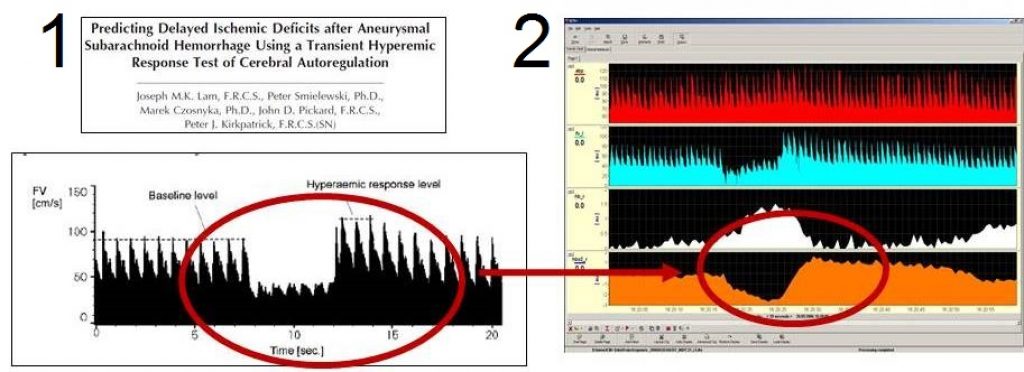
Autoregulation can be assessed intermittently using TCD with the transient hyperaemic response test (THRT, left). NIRS is helpful for continuous monitoring of Cox or TOx indices. It is unclear if it can be used for assessment with the THRT.
- Transcranial Doppler flow velocity (Fv) monitoring
- Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) oxygenation monitoring