Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has gained recognition in monitoring various organs, including the central nervous system. Research on NIRS has demonstrated the possibility of using it for quantifying cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume, making NIRS technology more appealing for real-time monitoring, in particular in the acute care setting. The most common applications of NIRS for cerebral monitoring include subarachnoid haemorrhage, TBI, carotid endarterectomy, cardiac surgery, as well as liver transplantation. ICM+ allows the continuous monitoring of NIRS parameters in the context of multimodal brain monitoring in several clinical conditions.
Cerebral autoregulation
NIRS has been extensively studied for the monitoring of cerebral autoregulation both in clinical, as well as experimental studies. Recent research has demonstrated that autoregulation indices based on NIRS parameters were highly correlated with those calculated with TCD or ICP.
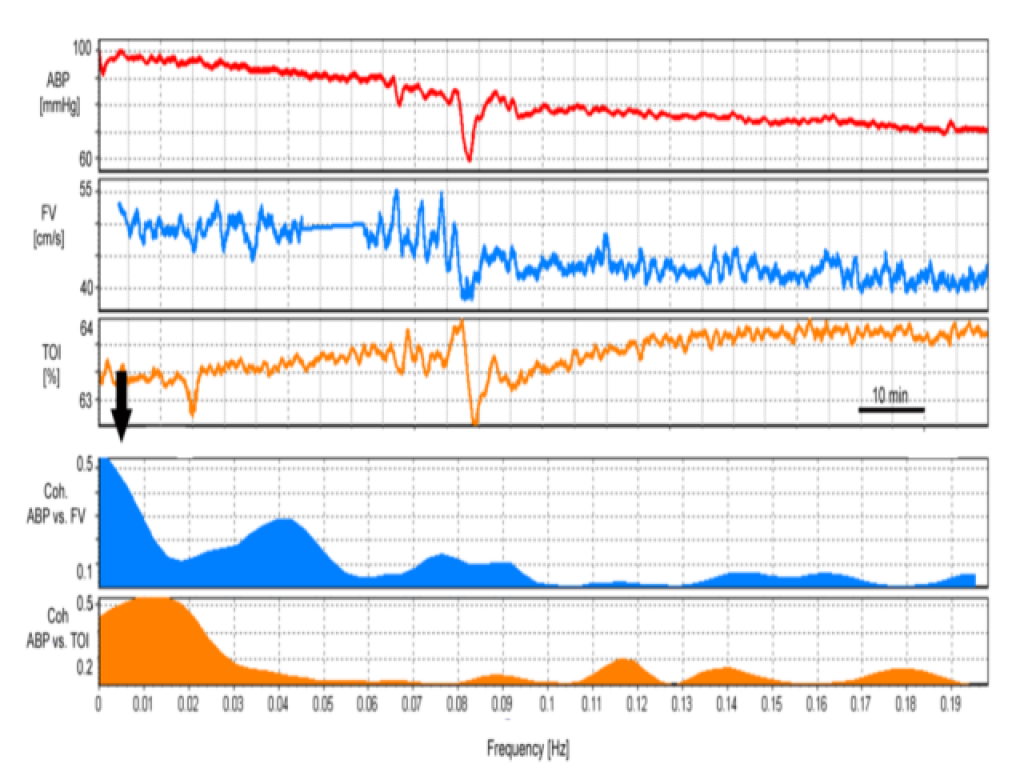
Monitoring data from a patient with SAH on day 5 post-ictus. High coherence between ABP and FV as well as between ABP and TOI (black arrow). ABP – arterial blood pressure; FV – flow velocity; SAH – subarachnoid haemorrhage; TOI – tissue oxygenation index obtained with NIRS. View image



