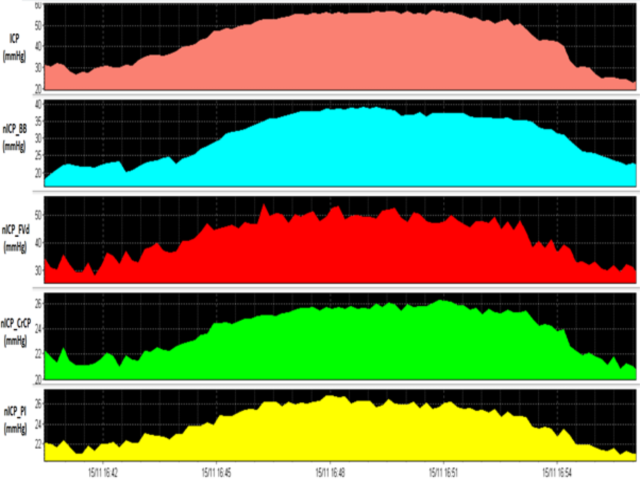
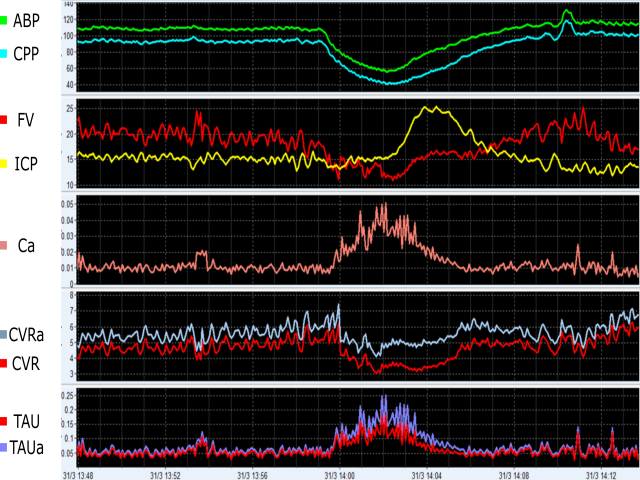
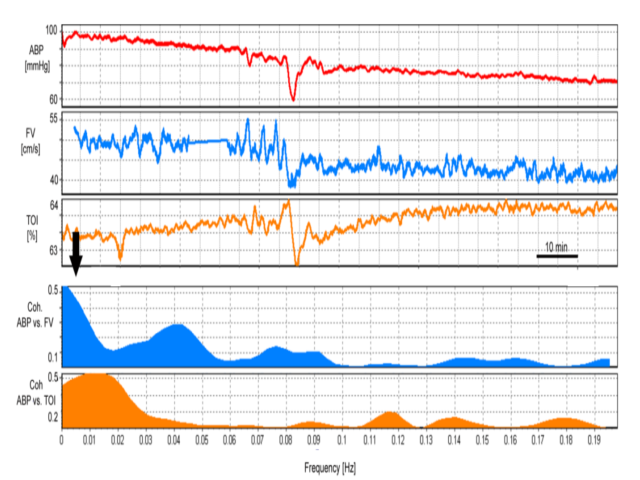
Non-invasive indices are mainly based on TCD and NIRS monitoring. Multi-parametric TCD (in conjunction with arterial blood pressure) may include: autoregulation indices, non-invasive ICP and CPP, critical closing pressure, and the cerebrovascular time constant (TAU). NIRS is ideal for long-term, non-invasive monitoring of cerebral autoregulation.